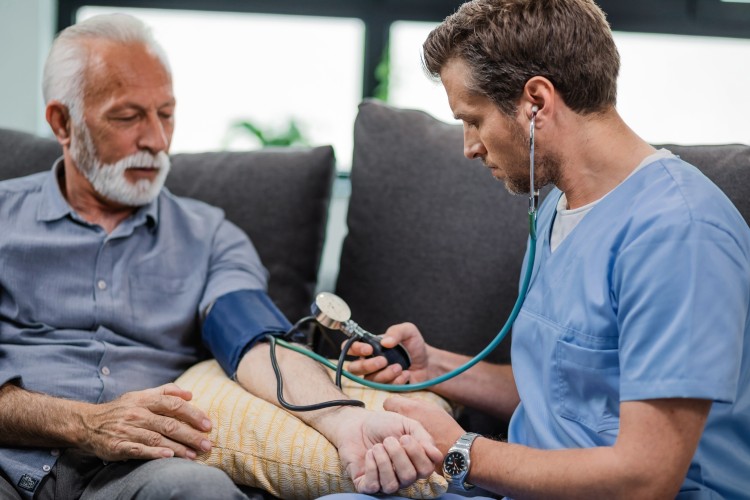
Doctors and nurses have different but important roles in healthcare. Doctors are like health detectives. They talk to patients, figure out what’s wrong, and make a plan for treatment. After about five years of medical school, they become experts in diagnosing and guiding a patient’s care.
Nurses are the doers. They carry out the plan made by the doctor. They give medicines, get patients ready for tests, and help with daily things like washing and eating. Nurses study for three years to learn practical skills and hands-on care.
So, doctors decide the big picture, and nurses make sure the day-to-day care happens. Both work together to keep patients healthy and happy.
What is a nurse?

A nurse is like a healthcare superhero! A nurse is a person who helps take care of sick or injured people. They work with a team of medical professionals in places like hospitals, doctor’s offices, or even at people’s homes.
Moreover, they do a lot of different tasks to help patients, like checking their vital signs, updating medical records, and dressing wounds. They might also give medications or injections and see how well a treatment is working.
Some specialize in certain types of care, like mental health, taking care of kids, helping pregnant women, or focusing on specific health issues like cancer or heart problems.
What is a doctor?
A doctor, also known as a physician, is a healthcare professional who helps people when they are sick or injured. They figure out what’s wrong with a person, give them the right treatment, and try to prevent illnesses. They can prescribe medicine, do surgeries, and work with other healthcare professionals like nurses to take care of patients.
Furthermore, there are different types of doctors. Some work in communities, like local doctors you might see when you’re not feeling well. Others specialize in certain areas like the brain (neurology), the bones (orthopedics), or kids (pediatrics). Doctors can also become experts in research to discover new things about medicine.
In a hospital, there are doctors called consultants who are in charge of taking care of patients. They are like the leaders of the medical team. Some are also teach and help train new doctors.
So, they are important because they help keep us healthy, treat us when we’re sick, and even make new discoveries to improve medicine.
Key Difference Between Doctors & Nurses
| Aspect | Doctors | Nurses |
| Job Role | Set the direction for patient’s care | More hands-on practical delivery of care |
| Education | Typically have a medical degree (MD or DO) | Obtain a nursing degree (e.g., RN, BSN) |
| Average Salary | £76,000 | £33,000 |
| Training Length | 5 years | 3 years |
| Career Progression | Robust pathways to top positions. | Limited and often more management roles. |
| Responsibility | Ultimately responsible for patient care. | Responsible just for personal actions. |
| Job Settings | Work in hospitals, clinics, and private practices. | Work in hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and community settings. |
Navigating Healthcare Roles: Distinctions Between Doctors and Nurses
In a hospital setting, doctors and nurses each play crucial roles in patient care. Take, for example, an eighty-year-old woman who arrived at A&E with abdominal pain.
Doctor’s Role:
The doctor takes the lead in understanding the patient’s condition. Through a conversation with the patient and a physical examination—such as feeling her abdomen—the doctor formulates a comprehensive plan. This plan may entail various investigations like scans or blood tests and the prescription of necessary medications. The doctor is ultimately responsible for setting the direction for the patient’s care.
Nurse’s Role:
On the other hand, the nurse executes the plan laid out by the doctor. This involves physically administering prescribed medications, including strong painkillers or anti-sickness drugs.
Additionally, the nurse ensures the patient is prepared for any scans ordered by the doctor. Nurses often serve as a patient’s initial point of contact and deliver hands-on care on the ward.
For instance, if the elderly lady stays in the ward for a few days, she often with the assistance of healthcare assistants, manages tasks like helping with hygiene, feeding, and addressing personal needs. This includes arranging for someone to care for her cat at home.
In this collaborative effort, the doctor’s role revolves around diagnosis and treatment planning, while the nurse’s role focuses on hands-on care and implementing the doctor’s recommendations. Together, they contribute to the well-being of the patient in a hospital environment.
Navigating the Paths to Healthcare Professions: Doctors vs. Nurses
Becoming a doctor or a nurse involves a comprehensive journey of learning scientific theory, clinical reasoning, and practical skills. While both paths lead to competent healthcare professionals, there are significant differences between the two.
To embark on a medical career , aspiring doctors must attend medical school, typically lasting 4-6 years at university. Entry to medical school is highly competitive, with stringent requirements.
Once enrolled, students face the challenges of an intense curriculum, demanding hard work and dedication. However, the rewarding outcome is graduating as a newly qualified doctor.
On the other hand, nursing studies at the university take a shorter route, usually three years. Despite the shorter duration, it’s not a leisurely stroll. The degree involves a rigorous apprenticeship-style model in the later stages of the course, resembling full-time work for nursing students, although without financial compensation.
Choosing it over medicine also offers some advantages. They also benefit from a more extensive selection of institutions, with 129 options compared to the 34 medical schools in the UK. Additionally, the academic entry requirements are lower, providing more flexibility with A-level results.
Undergraduate Training:
| Aspect | Doctors | Nurses |
| Course Length | 5 years | 3 years |
| Entry Requirements | AAA – A*AA | BCC – BBB |
| Cost Per Year | £9250 | £9250 |
| Number Of Universities Offering Course | 34 | 129 |
In summary, the journey to becoming a healthcare professional varies between doctors and nurses, with differences in duration, entry requirements, and the academic landscape.
Charting Career Progression: Doctors and Nurses in Healthcare
The journey into the healthcare profession unfolds for newly qualified doctors and nurses as they step out of university.
For doctors, the path involves navigating through foundation years, core training, and progressing as a registrar until achieving the esteemed position of a consultant. The duration to become a fully qualified doctor varies based on the specialty and the specific route taken.
Throughout this journey, they face challenging postgraduate exams, often more demanding than those encountered during medical school.
On the other hand, nurses follow a postgraduate progression outlined by the NHS banding system:
- Band 5: Newly qualified nurse
- Band 6: Nursing specialist or senior nurse
- Band 7: Advanced nurse/nurse practitioner
- Band 8: Modern matron or chief nurse
Starting at Band 5, nurses ascend through the bands over time, gaining experience and seniority. Towards the upper bands, nurses transition into more managerial roles, steering away from purely clinical responsibilities. At the pinnacle, roles like modern matron involve overseeing a substantial team while still engaging in various nursing duties.
Furthermore, perhaps the most notable distinction in the career progression of doctors and nurses lies in the flexibility of pathways. They can follow well-defined training routes, leading from a foundation year 1 doctor to a consultant surgeon who remains actively involved in surgeries and patient care.
In contrast, they often find themselves taking on more managerial responsibilities as they ascend in the NHS hierarchy. For those keen on preserving their clinical focus, an alternative pathway exists in becoming a nurse practitioner.
Navigating Salaries in Healthcare: Doctors vs. Nurses
When considering a career in either nursing or as a doctor, it’s essential to understand the salary differences between the two professions.
Average Annual Salaries:
- Doctors, on average, earn around £76,000 per year.
- Nurses, in contrast, have an average salary of £33,000 annually.
Both can choose to work either within the NHS or in private practice. However, doctors generally have a higher potential for lucrative earnings, especially if they establish a successful private practice.
NHS Base Pay Estimates (in £):
| Salary Category | Doctor | Nurse |
| Immediately after graduating | £29,000 | £26,000 |
| After 5 years | £51,000 | £39,000 |
| After 10 years | £85,000 | £47,000 |
| After 20 years | £101,000 | £66,000 |
It’s important to note that these figures represent the base pay within the NHS, and various factors can influence long-term career trajectories and earnings. Both have the option to take on extra shifts or work privately to supplement their income.
While doctors, particularly surgeons, may have more opportunities to establish a lucrative private practice—potentially doubling their take-home salary or more—experienced nurses can also boost their earnings by taking on extra shifts through bank agencies, earning over £50 per hour.
Despite differences in the avenues for additional income, the decision between nursing and a medical career often involves factors beyond monetary considerations.
Navigating the Distinctions: Doctors vs. Nurse Practitioners in Healthcare

Nurse practitioners, seasoned and highly qualified nurses, pivot towards clinical assessment rather than management as they advance. Operating at a mid-level comparable to a doctor with 3-5 years of experience, they bridge the gap between doctors and nurses, expanding their capabilities to encompass tasks typically handled by junior doctors.
So, this includes taking patient histories, making reasoned diagnoses, conducting blood tests and x-rays, prescribing medications (even controlled drugs), and working independently without supervision.
The disparities between doctors and nurse practitioners lie in their journey to the current position and their options for progression. Becoming a mid-level practitioner involves a doctor attending medical school and completing the foundation training program, a two-year stint as a junior doctor in various hospital departments.
In contrast, the path to becoming a nurse practitioner is more extensive. A nurse must first qualify, work in the field for 5-7 years, pursue a master’s degree, and obtain all the necessary prescribing qualifications.
Also, compared to the shorter duration of medical school and a few years of doctor training, this process makes the nurse practitioner route longer and more intricate.
Nurse practitioners typically achieve this senior role later in their careers, and clear promotion pathways from this position may not always be evident. Consequently, nurses often continue practicing in this capacity throughout their careers.
Conversely, they commonly aspire to progress from mid-level practitioners to higher-level roles or senior doctors. Following the relevant training pathways allows doctors to advance relatively seamlessly, provided they fulfill all the required training objectives.
Similarities Between Doctors Vs. Nurses
| Aspect | Doctors | Nurses |
| Patient Care | Both contribute to the overall well-being and treatment of patients | Both involved in hands-on patient care, monitoring health, and providing support |
| Healthcare Team | Integral members of the healthcare team | Essential members of the healthcare team, collaborate with each other and other healthcare professionals |
| Patient Advocacy | Advocate for patients’ health and well-being | Advocate for patients, ensuring their needs are met and rights are respected |
| Communication | Effective communication with patients,families, and other healthcare professionals | Communicate with patients, families, and other team members to ensure coordinated care |
| Continuous Learning | Commitment to ongoing education and staying updated on medical advancements | Emphasis on continuous learning, staying abreast of changes in healthcare practices |
| Team Collaboration | Collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care | Work collaboratively with doctors, pharmacists, therapists, and other team members for optimal patient outcomes |
| Compassion | Show compassion and empathy towards patients | Demonstrate compassion and empathy in providing emotional support to patients |
| Adaptability | Must adapt to changing patient conditions, medical advancements, and healthcare practices | Need to be adaptable to varying patient conditions, evolving healthcare practices, and dynamic healthcare environments |
| Stress Management | Deal with high-stress situations in diagnosing and treating complex illnesses | Encounter high-stress situations and emergencies, requiring effective stress management skills |
FAQ’s
What is the difference between a doctor and a nurse?
A doctor completes a four-year degree and a three-year residency program, while a nurse finishes a two- to four-year degree, both at accredited universities.
What do doctors do?
Doctors provide medical care, diagnosing and treating illnesses, injuries, and various health conditions.
What do nurses do?
Nurses offer patient care, working closely with doctors to provide treatment and support.
What is the difference between a doctor and a nurse in terms of education?
A doctor’s education involves a four-year degree and a three-year residency, while a nurse completes a two- to four-year degree at an accredited university.
What is the difference between a doctor and a nurse in terms of job responsibilities?
Doctors are responsible for diagnosing and treating health conditions, while nurses focus on providing care and support to patients.
Final Words
In conclusion, while doctors and nurses have distinct roles in healthcare, their collaboration is vital for comprehensive patient care. Doctors, with their extensive training and expertise, take the lead in diagnosing and planning treatment.
On the other hand, nurses through their hands-on care and implementation of doctors’ plans, ensure the well-being and comfort of patients.
So, together they form a dynamic team, each contributing unique skills to provide holistic and effective healthcare. The synergy between them underscores the importance of their partnership in delivering quality medical services and improving patient outcomes.